Difference between revisions of "Contrib/CompressibleMixingPhaseChangeFoam"
From OpenFOAMWiki
< Contrib
Mkraposhin (Talk | contribs) (→Model Equations) |
Mkraposhin (Talk | contribs) (→Model Equations) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
where <math>\hat \rho</math> computed with respect to previous formulations | where <math>\hat \rho</math> computed with respect to previous formulations | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | mixture density <math> \rho </math> calculated as | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\rho = \alpha_l \rho_l + \alpha_v \rho_v </math> | ||
| + | |||
* Liquid volume transport | * Liquid volume transport | ||
Let us consider transport of liquid (heavy phase) volume fraction <math>\alpha_l</math>: | Let us consider transport of liquid (heavy phase) volume fraction <math>\alpha_l</math>: | ||
| Line 63: | Line 69: | ||
\zeta \alpha_l \frac {d \rho_i}{dt} + \zeta \rho_i \frac {d \alpha_i}{dt} | \zeta \alpha_l \frac {d \rho_i}{dt} + \zeta \rho_i \frac {d \alpha_i}{dt} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Momentum equation (velocity prediction) | ||
| + | \frac {\partial \rho \textbf{U}}{\partial t} | ||
* Phase change model | * Phase change model | ||
| − | |||
* Energy equation | * Energy equation | ||
[http://www.os-cfd.ru/compressibleMixingPhaseChangeFoam/Solver.tgz Solver sources and tutorials located here] | [http://www.os-cfd.ru/compressibleMixingPhaseChangeFoam/Solver.tgz Solver sources and tutorials located here] | ||
Revision as of 20:54, 28 December 2012
Solver for two fluids with phase change (for example - water <---> steam), pressure and temperature density dependence
Model Equations
- Equation of state
Low-compressible fluid: 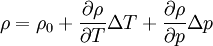
Ideal gas: 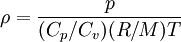
By combining this equations, we can get general relation:
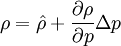
where 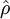 computed with respect to previous formulations
computed with respect to previous formulations
mixture density 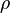 calculated as
calculated as
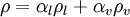
- Liquid volume transport
Let us consider transport of liquid (heavy phase) volume fraction 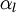 :
:
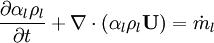
By converting to volume fluxes we get:
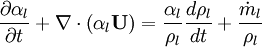
Using equation of state, we can reformulate substantial derivative for density in terms of pressure for any phase:
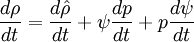
- General rule for converting from mass to volume fluxes in transport equation
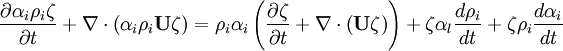
- Momentum equation (velocity prediction)
\frac {\partial \rho \textbf{U}}{\partial t}
* Phase change model * Energy equation