Difference between revisions of "Sig Turbulence / Dellenback Abrupt Expansion"
m (→Testcase description and experimental results) |
m (→Testcase description and experimental results) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
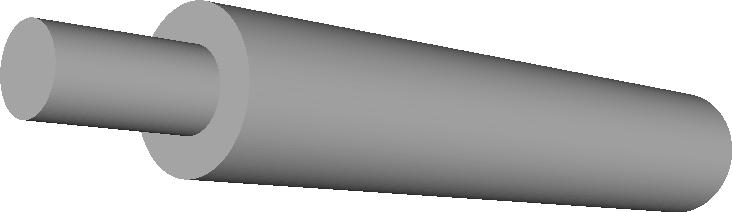
''Figure 1: Dellenback Abrupt Expansion geometry'' | ''Figure 1: Dellenback Abrupt Expansion geometry'' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
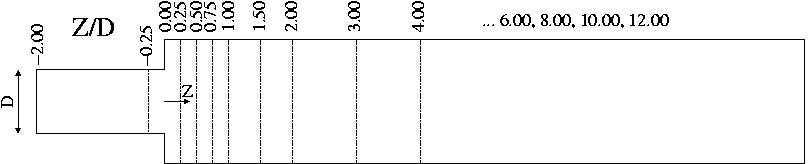
The measurements were taken at the cross-sections shown in figure 2. | The measurements were taken at the cross-sections shown in figure 2. | ||
| Line 61: | Line 40: | ||
* Most data sets show measurements on both sides of the centerline as a check for symmetry. | * Most data sets show measurements on both sides of the centerline as a check for symmetry. | ||
* All these experimental results are available in this case-study. | * All these experimental results are available in this case-study. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The geometric data used in this case-study are the following: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ::{| cellpadding="8" cellspacing="1" border="3" | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Inlet diameter | ||
| + | | <math> D_{in} = 50.78 mm </math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Outlet diameter | ||
| + | | <math> D_{out} = 98.5 mm </math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Expansion ratio | ||
| + | | <math> D_{out}/D_{in} = 1.94 </math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Inlet length | ||
| + | | <math> 2*D_{in} </math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Outlet length | ||
| + | | <math> 10*D_{in} </math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
Future work using this case-study should refer to Gyllenram and Nilsson [4], and Nilsson and Gyllenram [5]. | Future work using this case-study should refer to Gyllenram and Nilsson [4], and Nilsson and Gyllenram [5]. | ||
Revision as of 08:28, 25 May 2009
Contents
1 Testcase description and experimental results
Håkan Nilsson, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden
The turbulent swirling flow in an abrupt expansion was experimentally investigated by Dellenback, Metzger, and Neitzel [1]. The geometry is illustrated in Figure 1. The inlet is located at the smaller diameter, where either a pure axial, or swirling flow at different swirl and Reynolds numbers is imposed.
Figure 1: Dellenback Abrupt Expansion geometry
The measurements were taken at the cross-sections shown in figure 2.
Figure 2: Measurement cross-sections
Dellenback presented 9 cases: 3 with purely axial flow, and 6 with swirl:
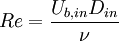
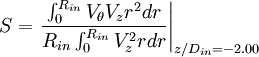
30,000 0.00, 0.60, 0.98 60,000 0.00, 1.16 100,000 0.00, 0.17, 0.74, 1.23
- Axial mean velocity profiles.
- Tangential mean velocity profiles.
- Axial RMS velocity profiles.
- Tangential RMS velocity profiles.
- Most data sets show measurements on both sides of the centerline as a check for symmetry.
- All these experimental results are available in this case-study.
The geometric data used in this case-study are the following:
Inlet diameter 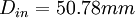
Outlet diameter 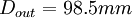
Expansion ratio 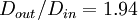
Inlet length 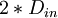
Outlet length 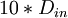
Future work using this case-study should refer to Gyllenram and Nilsson [4], and Nilsson and Gyllenram [5].
2 Published computational results
Computations have been performed by Schluter et al. [2], Gyllenram, Nilsson and Davidson [3], Gyllenram and Nilsson [4,5], and Gyllenram [6]. Gyllenram and Nilsson [4] validates a filtered k-omega SST model using this test case. Nilsson and Gyllenram [5] implemented the kOmegaSSTF model in OpenFOAM, and validated it using this test case.
3 References
[1] Dellenback, P.A., Metzger, D.E., and Neitzel, G.P., "Measurements in Turbulent Swirling Flow Through an Abrupt Expansion", AIAA Journal, 26(6), pp.669-681 , 1987.
[2] Schluter, J.U., Pitsch, H., and Moin, P., "Large Eddy Simulation Inflow Conditions for Coupling With Reynolds-Averaged Flow Solvers", AIAA Journal, 42(3), pp. 478-484, 2004.
[3] Gyllenram, W., Nilsson, H., and Davidson, L., "Large Eddy Simulation of Turbulent Swirling Flow Through a Sudden Expansion", IAHR 2006, Yokohama, 2006, Paper, Slides
[4] Gyllenram, W., and Nilsson, H., "Design and Validation of a Scale-Adaptive Filtering Technique for LRN Turbulence Modeling of Unsteady Flow", Journal of Fluids Engineering, May 2008, Vol 130.
[5] Nilsson, H., and Gyllenram, W., "Experiences with OpenFOAM for water turbine applications", 1st OpenFOAM Conference, Old Windsor, London, 2007. Paper, Slides
[6] Gyllenram, W., "Analytical and Numerical Studies of Internal Swirling Flows", PhD Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2008, ISBN 978-91-7385-104-6, CPL, Thesis, Errata, Slides
4 How to get the files
The OpenFOAM Dellenback Abrupt Expansion cases described in the following sections were developed as a case-study for the Fourth OpenFOAM Workshop, Montréal, 2009, and can be found at the OpenFOAM-extend SourceForge project. It includes complete OpenFOAM cases that solve the flow in the domain (2D) and automatic post-processing of the results. The block-structured hexahedral meshes are parameterized and generated with m4 and blockMesh. Instructions on how to run the cases follow below.
Get all the current case files by doing:
cd $FOAM_RUN svn checkout http://openfoam-extend.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/openfoam-extend/trunk/Breeder_1.5/OSIG/Turbulence/dellenbackAbruptExpansion
In the descriptions below, we thus assume that the dellenbackAbruptExpansion directory is located in the $FOAM_RUN directory
Update your files every now and then by doing:
cd $FOAM_RUN/dellenbackAbruptExpansion svn update
See further info at OpenFOAM-extend webpage
You will also need the profile1DfixedValue boundary condition. To install and use it, see Sig Turbomachinery Library OpenFoamTurbo
5 Directory structure
The structure of the dellenbackAbruptExpansion directory is as follows:
Coming soon: print-out from 'tree' command.
- The "cases" directory contains the different test cases.
- The "measurements" directory contains all the data measured by Dellenback et al. [1]. The data is re-arranged to facilitate the automatic post-processing.
Here is what you can find in the "cases" directory:
Coming soon: print-out from 'tree' command.
All cases have the same sub-directory structure. Here is an example based on the ??? case:
Coming soon: print-out from 'tree' command.
You can contribute cases if you come up with more ideas. In that case, please try to follow the same directory structure and name conventions. Add instructions on the new cases in this Wiki.
6 Test cases
6.1 DAEkEpsilon
6.2 DAEtransientkOmegaSSTF
7 Others
Back to Sig Turbulence
Back to Top