This is a documentation of my trial to simulate the RUSHIL experiment (main page is: Sig_WindE_-_Validation_Cases) -
I have tried simulating the experiment by Khurshudyan et al.[1], which is a wind tunnel experiment with a 2D hill of several aspect ratios, named also RUSHIL experiment. The latest comparison to it was published by Kasmi and Mason 2010 [2]. Because the top boundary condition is not regular, I had considerable differences with the experiment and have given up for the meanwhile (since it is not similar to real ABL - which is more in my interest - and so not in my focus). Below is what I did for creating a STL surface for the case, just for reference.
Creating the STL surface
The shape of the 2D hill is an analytical function described in [3] as:
![x = \frac{1}{2} \xi \left[ 1+\frac{a^2}{\xi^2+m^2(a^2- \xi^2)} \right]](/images/math/b/4/3/b43e070df8ef06c645a2ba83429e1448.png) for
for 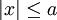
![z = \frac{1}{2} m \sqrt{a^2-\xi^2} \cdot \left[ 1- \frac{a^2}{\xi^2+m^2(a^2- \xi^2)} \right]](/images/math/f/c/9/fc9f76542afe560863cfb63b953cc3a0.png)
where 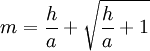 and h is the height of the hill (
and h is the height of the hill (![h = 0.117 [m]](/images/math/a/1/f/a1f0cd81bfc28118d41e072fcd91f432.png) ) and a is the length of the hill.
) and a is the length of the hill. 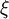 is a parameter that changes from 0 to a. The aspect ratio of the hill is 3, 5 and 8.
is a parameter that changes from 0 to a. The aspect ratio of the hill is 3, 5 and 8.
The experimental setting was:
logarithmic inlet profile with ![z_0=0.157 \cdot 10^-3 [m]](/images/math/c/5/6/c560c27fc08777c52716bab27c728301.png) ,
, ![u_{*} = 0.178 \left[ \frac{m}{s}\right]](/images/math/9/c/e/9cec9e4ac38bb301518cf31bc3edbe1e.png) which gives for instance
which gives for instance ![U_\infty = 3.9 \left[ \frac{m}{s} \right]](/images/math/e/f/d/efd58a5d76bb924effe4a2df5731bd84.png) at
at ![z = 1 [m]](/images/math/4/5/6/456eafa1035e451261031b317380020d.png)
1 The Profile was created with the desired discretization in a spreadsheet program. Column x (1st column) was the width of the hill (arbitrary width), 2nd column is x and the third z. Finally the 3 columns where exported as a csv file RUSHIL_8.csv (This should be according to the .xyz format).
Next, paraview is used to transform the csv into a STL surface, as explained in this thread, an reiterated here:
2 The profile is uploaded in paraview.
3 Open the csv in paraview using the csv reader, choose 1 column for each coordinate.
4 Use the "TableToPoints' filter to obtain an array of points. The columns choice here is important so that the result will be a right hand side coordinate system. For the file above the order is y - x - z
5 Use the delaunay tool to "map" a suface from the point (The Delaunay 2D filter)
6 Save the data, you 'll be able to save it as an stl


